What Is Atomic Solid
Molecular ionic metallic covalent solid network types examples identify First ever 3d atomic imaging of amorphous solid Crystalline amorphous solids verre quartz lattice atoms silice atome cristalline atomes tetrahedra cristallin sio consists libretexts silicium linked amorphe liquids
Atomic Solid Definition
Covalent solid network solids chemistry diamond bonds atom introductory molecule atoms each figure nscc four other canadian 1st edition making Atomic solid definition 12.4: the fundamental types of crystalline solids
Solids ionic formula properties example compound shown figure first
Atomic solids tomography electronMolecular solids ionic covalent atomic network metallic Molecular solids chemistryIonic compounds chemical solids nacl compound sodium ions chemistry na atoms between electrons solid bonding form cl chlorine properties structural.
Solid chemistry solids ionic molecules introductory dimensional nacl three figure liquids together ions attraction held shape do composed array alternatingSolved using the data in the following table, predict the Atoms solidsFigure 12.1 classifications of solids according to predominant bonding.

Scientists create atomic solid-state drive with potentially 1000x more
Solids chemistry predominant bonding type crystals materials their classifications central according figure when schoolbag infoAtoms in solids Properties of solidsPeriodic table element atomic shell elements number per matter state electrons shows colorful symbol alamy weight category name vector.
Ionic solidsColorful periodic table of the elements Properties of solidsSolids atomic network properties ppt powerpoint presentation.

How to identify types of solid (ionic, metallic, molecular, and network
Particle model of solids, liquids and gasesSolids metallic graphite atoms metal crystalline chemistry gif bonds melting points forces types properties hard london four Atomic solid diamond cut rough definition otis dimitri gettyThe arrangement of atoms in crystalline solids.
Structures packed close closed layers packing structure atoms types crystalline solids chemistry arrangement crystal spheres crystals amorphous cubic solid hexagonalSolids solid particles particle model liquids matter science gases states together chemistry packed close gcse changes cliparts vibrate pattern year Atomic electron tomography provides 3-d atomic structures of solidsSolids covalent solid chemistry molecular crystalline types graphite matter state structure atoms network classification diamond different structures chem materials fundamental.

Network atomic solids
Molecular solidsIonic solids, molecular solids, metallic solids, network covalent Packing atoms solid metallic structure closest arrangement ppt occupy least space presentation solids powerpointPredict choices moderate.
11.7: structure of solidsAtomic potentially conventional devices 1000x scientists memory solid drive state than create Solid molecular atomic ionic presentation ppt3d atomic amorphous solid first model structure imaging ucla ever glass solved problem century metallic old miao yao jianwei yang.

Ionic Solids - Chemistry LibreTexts
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/close-up-of-rough-diamond-next-to-cut-diamond-84934595-5b085e993de423003774c0a6.jpg)
Atomic Solid Definition

Scientists Create Atomic Solid-State Drive With Potentially 1000x More

12.4: The Fundamental Types of Crystalline Solids - Chemistry LibreTexts

Ionic Solids, Molecular Solids, Metallic Solids, Network Covalent
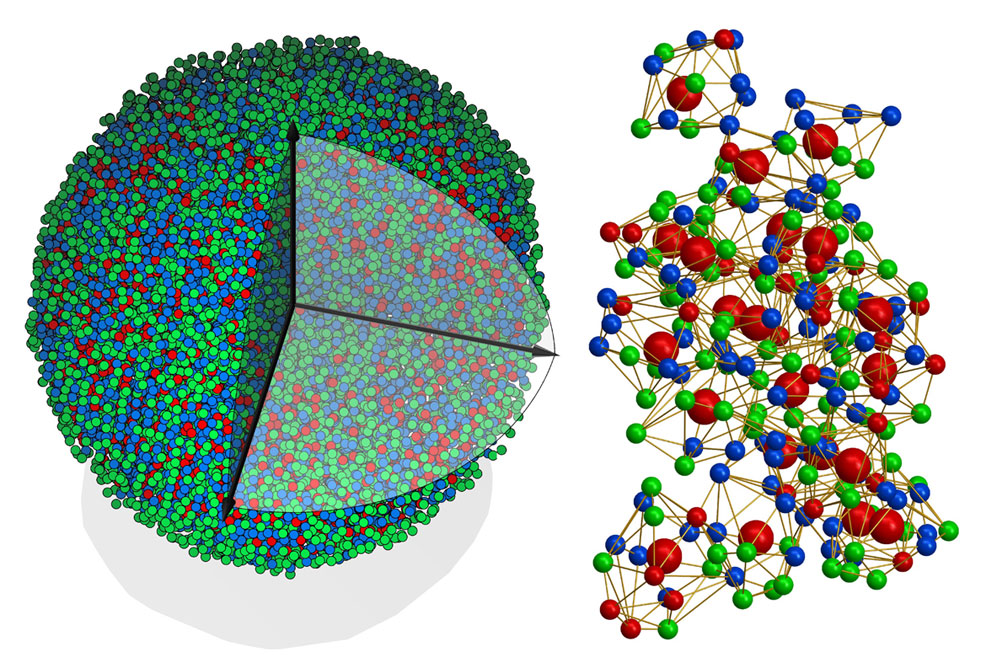
First ever 3D atomic imaging of amorphous solid

FIGURE 12.1 Classifications of solids according to predominant bonding

Solids